Did You Know?
Cord Blood transplants have been around for over 30 years2, with the world’s first Cord Blood transplant taking place in October 19883.
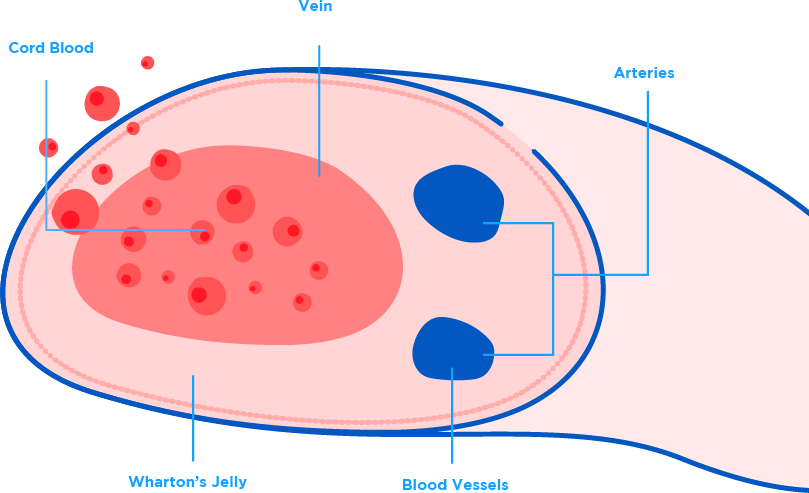
Cord blood is the blood found in the baby’s umbilical cord, it is a rich source of Haemopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs). These stem cells make up the building blocks in our blood and immune system throughout our life. A baby’s own cord blood guarantees a perfect match for him/her. The cord blood can also potentially increase the chances of having a match for his/her siblings and parents.
The HSCs in Cord Blood can develop into all types of blood cells. These Stem Cells are similar to those found in an adult’s bone marrow and are clinically proven to be used in the treatment of more than 80 diseases1, such as blood disorders, certain childhood & blood cancers, metabolic disorders and immunodeficiency syndrome.
Doctors believe there is more potential, and research is ongoing to use Cord Blood to treat other diseases including Autism, Cerebral Palsy, Diabetes, Heart Disease, Strokes, and more1. By storing your baby’s Cord Blood today, you will be able to tap on the new and ongoing medical advances in Regenerative Therapy and Cell & Gene Therapy.
A 100% match for your baby
Eliminates difficulties in finding a compatible donor
The sample is readily available, meaning no treatment delays and any potential disease progression can be avoided
It has the potential to be used as treatment options for family members
Cord Blood from a related donor will result in fewer complications and improved medical outcomes

Cord blood banking is an invaluable opportunity for parents to secure their child’s future health. The process involves collecting and storing the stem cells found in the umbilical cord blood, which can be used in the treatment of various life-threatening diseases1. With medical advancements continuously evolving, the potential applications of stem cells are expanding, making cord blood banking a crucial consideration for new parents.
An autologous transplant, or transplant where the patient is their own donor, will have a lower risk of life-threatening complications. There is no risk of graft versus host disease (GVHD) and no need for the patient to undergo immunosuppressive therapy.
Where the patient receives his/her own stem cells.
Patient receives stem cells from a matching donor. Probability of a match is much higher among siblings and direct family members.
Name of Disease/Disorder |
Cord Blood Autologous |
Cord Blood Allogeneic |
|
| Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) |
|
||
| Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AMLs) |
|
||
| Multiple Myeloma |
|
|
|
| Plasma Cell Leukemia |
|
|
|
| Hodgkin's Lymphoma |
|
|
|
| Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma |
|
|
|
| Aplastic Anemia |
|
|
|
| Fanconi Anemia |
|
||
| Congenital Dyserythropoietic Anemia |
|
||
| Sickle Cell Disease |
|
||
| Beta Thalassemia Major |
|
||
| Neuroblastoma |
|
||
| Medulloblastoma |
|
||
The full list of diseases can be obtained from https://parentsguidecordblood.org/en/diseases
There are more than 1,000 clinical trials underway for Stem Cell therapies and treatments6.
With rapid advances in stem cell research, treatment methods using Cord Blood have the potential to change and save lives.
Read more about Cord Stem Cells
Name of Disease/Disorder |
Cord Blood Autologous |
Cord Blood Allogeneic |
| Alzheimer's Disease |
|
|
| Autism |
|
|
| Cerebral Palsy |
|
|
| Hearing Loss (Acquired Sensorineural) |
|
|
| Parkinson's Disease |
|
|
| Spinal Cord Injury |
|
|
| Stroke |
|
|
| Traumatic Brain Injury |
|
|
| Crohn’s Disease |
|
|
| Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) |
|
|
| Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD) |
|
|
| Lupus |
|
|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis |
|
| Surgery for Congenital Heart Defects |
|
| Diabetes, Type 1 (Auto Immune) |
|
|
| Diabetes, Type 2 |
|
|
| Liver Cirrhosis |
|
|
| Liver Failure |
|
The full list of diseases can be obtained from https://parentsguidecordblood.org/en/diseases
Private cord blood banking offers security and peace of mind, knowing that stem cells are readily available for potential medical use. Some key benefits include:
Understanding how cord blood banking works can help parents make an informed decision. The process involves these key steps8:
Cord blood is collected immediately after birth, ensuring that the process is painless and non-invasive for both mother and baby
The collected blood undergoes laboratory processing to separate and concentrate stem cells while removing unnecessary components.
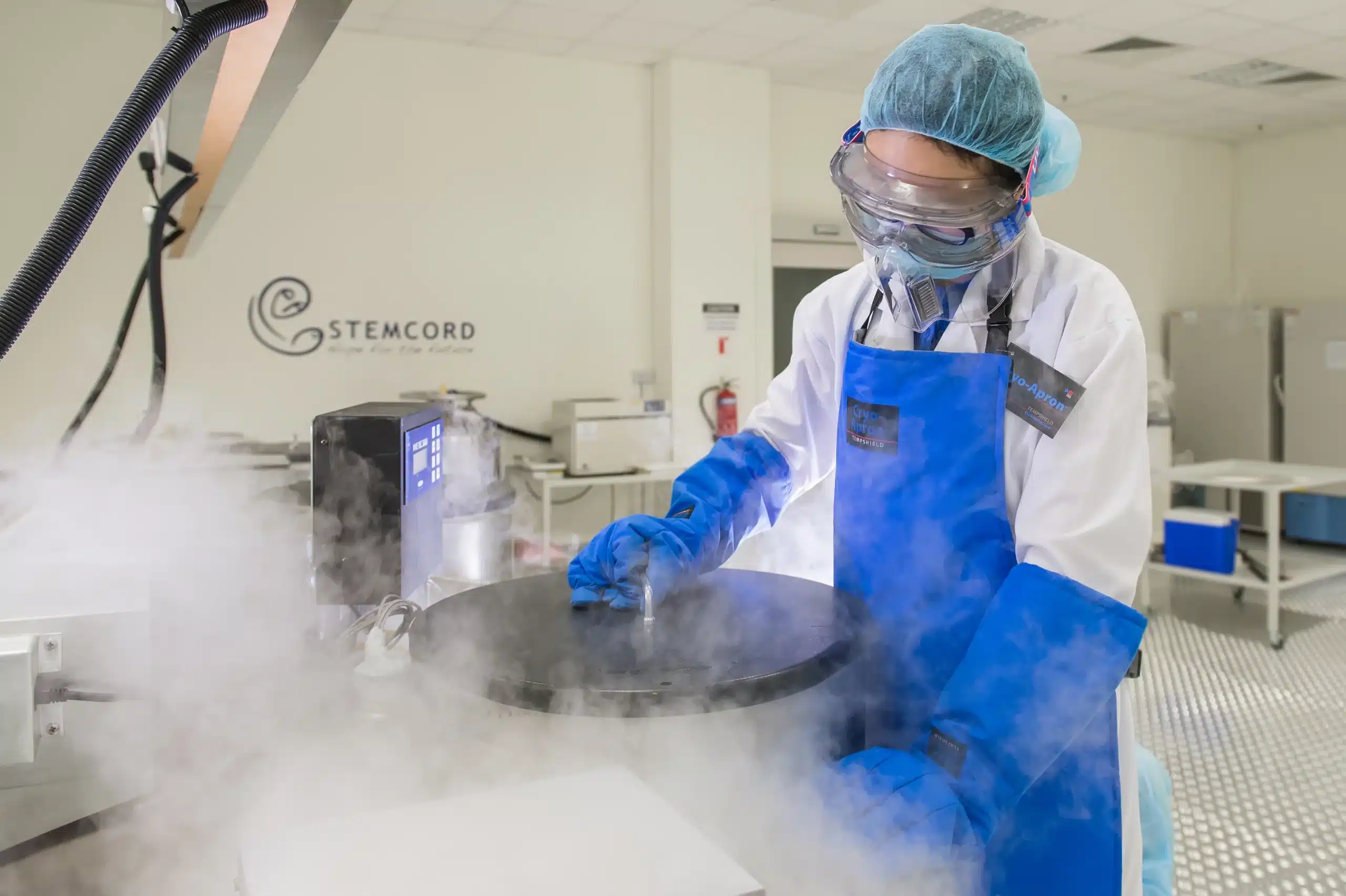

The stem cells are then stored at ultra-low temperatures in specialized cryogenic tanks, preserving their viability for future medical use.
In the event of a medical need, stored stem cells can be quickly retrieved and used for treatment.

Medical professionals and researchers recommend cord blood banking due to its life-saving potential. According to HealthHub, here are some expert-backed reasons why parents should consider storing their baby’s cord blood:
Many families view this as a vital investment in their child’s health. The decision to store cord blood today can provide life-saving treatment options in the future. Contact us to know the cost of cord blood banking.

There are several misconceptions surrounding cord blood banking. Let’s debunk some of the most common myths:
Cord blood banking is a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to safeguard your child’s health. With extensive medical applications and ongoing research, storing your baby’s cord blood is a decision that could provide life-saving treatments in the future.
Take the first step today! Contact Us to speak with an expert.
Today, scientifically it is proven that the storage of cord blood can stretch over 23 years. Many studies have shown that as long as it is properly stored, Cord Blood can be stored indefinitely.
Yes, sibling matches are more likely to be compatible, making stored cord blood a valuable resource for family use.
If not stored, cord blood is typically discarded as medical waste. Choosing to bank it preserves a valuable medical resource.
No, the process is painless and non-invasive for both mother and baby.
Simply register with a private cord blood bank before your due date to ensure a smooth process at birth.
In some cases, stored cord blood can be a match for parents or extended family members, depending on genetic compatibility.
Cord blood collection is completely safe for both mother and baby. The procedure is performed by trained healthcare professionals and does not interfere with the birthing process. Additionally, private banks follow strict guidelines to ensure the proper handling and storage of stem cells.
Banking cord blood does not guarantee that the cells will provide a cure or be applicable for every situation. The treating physician will determine the ultimate use. There is no guarantee that the umbilical cord blood will be a match for a family member or will provide a cure. Autologous cord blood stem cells will not guarantee suitable treatment for all inherited genetic diseases. As with any transplant therapy, therapeutic success depends upon many factors beyond the stem cells themselves including patient condition, type of disease, recipient-donor relationship and matching, and other factors. The use of cord blood stem cells for emerging treatments is experimental. Please consult your physician.